Python-сообщество
Форум сайта python.su
- Вы не вошли.
Уведомления
- Начало
- » Инструментальные средства разработки
- » Pydev + IPython
![[RSS Feed] [RSS Feed]](/static/djangobb_forum/img/feed-icon-small.png)
#1 Дек. 17, 2018 22:46:04
- @cckyi_boxxx
-

-
- От:
- Зарегистрирован: 2012-01-13
- Сообщения: 181
- Репутация:
 14
14 
- Профиль Отправить e-mail
Pydev + IPython
задача проста, прикрутить консоль IPython к Pydev в Aptana studio, к последней уже привык и перескакивать уже не хочется, выбор на нее пал в основном из-за очень удобного для меня интерфейса и автоматически всплывающих коментов к функциям при автодополнении для меня это экономит уйму времени т.к. не надо читать доки к еще не знакомым либам, просто нашел нужную и юзаешь сразу, первое время пролистывая всю ее стрелками, пока не отпечатается в памяти. (см фото)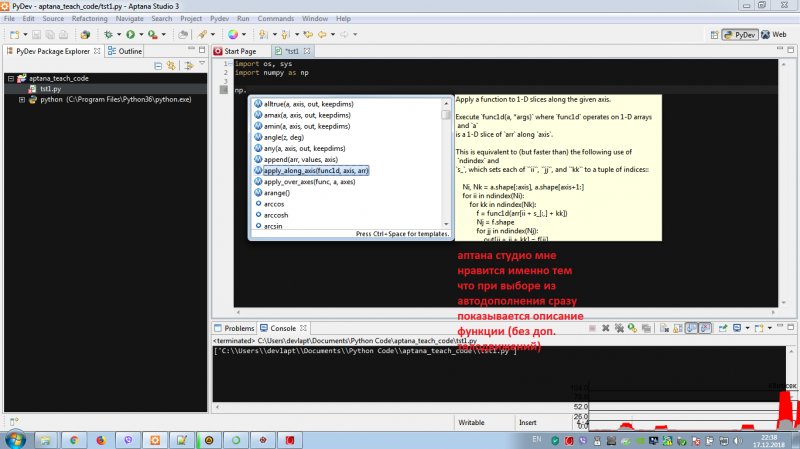
сейчас-же взялся за изучение нейросетей и работы с большими обьемами данных, и наткнулся на то что большинство работает в ipython, многие его фичи мне понравились но полностью перейти на работу в консоли или в юпитер нотбуке я не готов, глянул встроенную в анаконду иде - spyder и в ней все меня порадовало , но из-за отсутствия этик окошек с описанием функций и переменных модулей я от нее отказался (см фото) 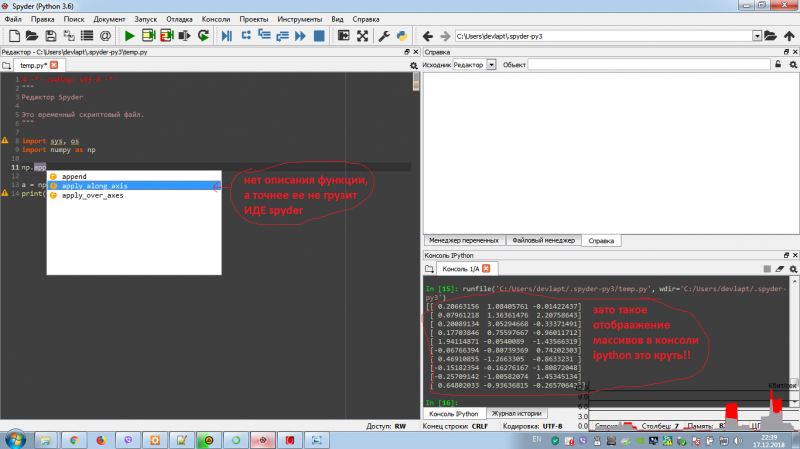
а теперь внимание вопрос, есть-ли способ прикрутить к аптане (pydev) ipython так-же как он прикручен в спайдере, искал инфу в инете но ничего не нашел, мб у кого из форумчан есть опыт ?
Отредактировано @cckyi_boxxx (Дек. 17, 2018 22:47:21)
Офлайн
#2 Дек. 18, 2018 10:19:37
- PEHDOM
-

-

- Зарегистрирован: 2016-11-28
- Сообщения: 2196
- Репутация:
 294
294 
- Профиль Отправить e-mail
Pydev + IPython
http://www.pydev.org/manual_101_interpreter.html
не?
To configure the interpreter:
1. Go to: window > preferences > PyDev > Interpreter - (Python/Jython/IronPython).
2. Choose the interpreter you have installed in your computer (such as python.exe, jython.jar or ipy.exe).
…..
==============================
Помещайте код в теги:
[code python][/code]
Отредактировано PEHDOM (Дек. 18, 2018 10:21:19)
Офлайн
#3 Дек. 21, 2018 18:42:32
- @cckyi_boxxx
-

-
- От:
- Зарегистрирован: 2012-01-13
- Сообщения: 181
- Репутация:
 14
14 
- Профиль Отправить e-mail
Офлайн
#4 Дек. 22, 2018 10:30:27
- PEHDOM
-

-

- Зарегистрирован: 2016-11-28
- Сообщения: 2196
- Репутация:
 294
294 
- Профиль Отправить e-mail
Pydev + IPython
@cckyi_boxxxну так оно вам говорит что не может получить информацию про интерпретатор. Наиболее общие причины:
вот что вылазит
-Ииспользуеться неподдерживаемая версия..
-Указан неправильный интерпретатор….
И вообще нужно смотреть лог ошибок для детальной информации.
Вот и покажите что вам в логах пишет.
==============================
Помещайте код в теги:
[code python][/code]
Офлайн
#5 Дек. 22, 2018 11:51:05
- @cckyi_boxxx
-

-
- От:
- Зарегистрирован: 2012-01-13
- Сообщения: 181
- Репутация:
 14
14 
- Профиль Отправить e-mail
Pydev + IPython
вкладка “details”
See error log for details.
Unable to recreate the Interpreter info (Its format changed. Please, re-create your Interpreter information).Contents found:=========
IPython
=========
Tools for Interactive Computing in Python
=========================================
A Python shell with automatic history (input and output), dynamic object
introspection, easier configuration, command completion, access to the
system shell and more. IPython can also be embedded in running programs.
Usage
ipython [subcommand] [options] [-c cmd | -m mod | file] [--] [arg] ...
If invoked with no options, it executes the file and exits, passing the
remaining arguments to the script, just as if you had specified the same
command with python. You may need to specify `--` before args to be passed
to the script, to prevent IPython from attempting to parse them. If you
specify the option `-i` before the filename, it will enter an interactive
IPython session after running the script, rather than exiting. Files ending
in .py will be treated as normal Python, but files ending in .ipy can
contain special IPython syntax (magic commands, shell expansions, etc.).
Almost all configuration in IPython is available via the command-line. Do
`ipython --help-all` to see all available options. For persistent
configuration, look into your `ipython_config.py` configuration file for
details.
This file is typically installed in the `IPYTHONDIR` directory, and there
is a separate configuration directory for each profile. The default profile
directory will be located in $IPYTHONDIR/profile_default. IPYTHONDIR
defaults to to `$HOME/.ipython`. For Windows users, $HOME resolves to
C:\Users\YourUserName in most instances.
To initialize a profile with the default configuration file, do::
$> ipython profile create
and start editing `IPYTHONDIR/profile_default/ipython_config.py`
In IPython's documentation, we will refer to this directory as
`IPYTHONDIR`, you can change its default location by creating an
environment variable with this name and setting it to the desired path.
For more information, see the manual available in HTML and PDF in your
installation, or online at http://ipython.org/documentation.html.
Subcommands
-----------
Subcommands are launched as `ipython cmd [args]`. For information on using
subcommand 'cmd', do: `ipython cmd -h`.
profile
Create and manage IPython profiles.
kernel
Start a kernel without an attached frontend.
locate
print the path to the IPython dir
history
Manage the IPython history database.
qtconsole
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Launch the Jupyter Qt Console.
notebook
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Launch the Jupyter HTML Notebook Server.
console
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Launch the Jupyter terminal-based Console.
nbconvert
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Convert notebooks to/from other formats.
trust
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Sign notebooks to trust their potentially unsafe contents at load.
kernelspec
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Manage Jupyter kernel specifications.
install-nbextension
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Install Jupyter notebook extension files
Options
-------
Arguments that take values are actually convenience aliases to full
Configurables, whose aliases are listed on the help line. For more information
on full configurables, see '--help-all'.
--debug
set log level to logging.DEBUG (maximize logging output)
--quiet
set log level to logging.CRITICAL (minimize logging output)
--init
Initialize profile with default config files. This is equivalent
to running `ipython profile create <profile>` prior to startup.
--autoindent
Turn on autoindenting.
--no-autoindent
Turn off autoindenting.
--automagic
Turn on the auto calling of magic commands. Type %%magic at the
IPython prompt for more information.
--no-automagic
Turn off the auto calling of magic commands.
--pdb
Enable auto calling the pdb debugger after every exception.
--no-pdb
Disable auto calling the pdb debugger after every exception.
--pprint
Enable auto pretty printing of results.
--no-pprint
Disable auto pretty printing of results.
--color-info
IPython can display information about objects via a set of functions,
and optionally can use colors for this, syntax highlighting
source code and various other elements. This is on by default, but can cause
problems with some pagers. If you see such problems, you can disable the
colours.
--no-color-info
Disable using colors for info related things.
--nosep
Eliminate all spacing between prompts.
--pylab
Pre-load matplotlib and numpy for interactive use with
the default matplotlib backend.
--matplotlib
Configure matplotlib for interactive use with
the default matplotlib backend.
--autoedit-syntax
Turn on auto editing of files with syntax errors.
--no-autoedit-syntax
Turn off auto editing of files with syntax errors.
--simple-prompt
Force simple minimal prompt using `raw_input`
--no-simple-prompt
Use a rich interactive prompt with prompt_toolkit
--banner
Display a banner upon starting IPython.
--no-banner
Don't display a banner upon starting IPython.
--confirm-exit
Set to confirm when you try to exit IPython with an EOF (Control-D
in Unix, Control-Z/Enter in Windows). By typing 'exit' or 'quit',
you can force a direct exit without any confirmation.
--no-confirm-exit
Don't prompt the user when exiting.
--term-title
Enable auto setting the terminal title.
--no-term-title
Disable auto setting the terminal title.
--classic
Gives IPython a similar feel to the classic Python prompt.
--quick
Enable quick startup with no config files.
-i
If running code from the command line, become interactive afterwards.
It is often useful to follow this with `--` to treat remaining flags as
script arguments.
--profile-dir=<Unicode> (ProfileDir.location)
Default: ''
Set the profile location directly. This overrides the logic used by the
`profile` option.
--profile=<Unicode> (BaseIPythonApplication.profile)
Default: 'default'
The IPython profile to use.
--ipython-dir=<Unicode> (BaseIPythonApplication.ipython_dir)
Default: ''
The name of the IPython directory. This directory is used for logging
configuration (through profiles), history storage, etc. The default is
usually $HOME/.ipython. This option can also be specified through the
environment variable IPYTHONDIR.
--log-level=<Enum> (Application.log_level)
Default: 30
Choices: (0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 'DEBUG', 'INFO', 'WARN', 'ERROR', 'CRITICAL')
Set the log level by value or name.
--config=<Unicode> (BaseIPythonApplication.extra_config_file)
Default: ''
Path to an extra config file to load.
If specified, load this config file in addition to any other IPython config.
--autocall=<Enum> (InteractiveShell.autocall)
Default: 0
Choices: (0, 1, 2)
Make IPython automatically call any callable object even if you didn't type
explicit parentheses. For example, 'str 43' becomes 'str(43)' automatically.
The value can be '0' to disable the feature, '1' for 'smart' autocall, where
it is not applied if there are no more arguments on the line, and '2' for
'full' autocall, where all callable objects are automatically called (even
if no arguments are present).
--colors=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShell.colors)
Default: 'Neutral'
Choices: ['Neutral', 'NoColor', 'LightBG', 'Linux']
Set the color scheme (NoColor, Neutral, Linux, or LightBG).
--logfile=<Unicode> (InteractiveShell.logfile)
Default: ''
The name of the logfile to use.
--logappend=<Unicode> (InteractiveShell.logappend)
Default: ''
Start logging to the given file in append mode. Use `logfile` to specify a
log file to **overwrite** logs to.
-c <Unicode> (InteractiveShellApp.code_to_run)
Default: ''
Execute the given command string.
-m <Unicode> (InteractiveShellApp.module_to_run)
Default: ''
Run the module as a script.
--ext=<Unicode> (InteractiveShellApp.extra_extension)
Default: ''
dotted module name of an IPython extension to load.
--gui=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShellApp.gui)
Default: None
Choices: ['glut', 'gtk', 'gtk2', 'gtk3', 'osx', 'pyglet', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'wx', 'gtk2', 'qt4']
Enable GUI event loop integration with any of ('glut', 'gtk', 'gtk2',
'gtk3', 'osx', 'pyglet', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'wx', 'gtk2', 'qt4').
--pylab=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShellApp.pylab)
Default: None
Choices: ['auto', 'agg', 'gtk', 'gtk3', 'inline', 'ipympl', 'nbagg', 'notebook', 'osx', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'widget', 'wx']
Pre-load matplotlib and numpy for interactive use, selecting a particular
matplotlib backend and loop integration.
--matplotlib=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShellApp.matplotlib)
Default: None
Choices: ['auto', 'agg', 'gtk', 'gtk3', 'inline', 'ipympl', 'nbagg', 'notebook', 'osx', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'widget', 'wx']
Configure matplotlib for interactive use with the default matplotlib
backend.
--cache-size=<Int> (InteractiveShell.cache_size)
Default: 1000
Set the size of the output cache. The default is 1000, you can change it
permanently in your config file. Setting it to 0 completely disables the
caching system, and the minimum value accepted is 3 (if you provide a value
less than 3, it is reset to 0 and a warning is issued). This limit is
defined because otherwise you'll spend more time re-flushing a too small
cache than working
To see all available configurables, use `--help-all`
Examples
--------
ipython --matplotlib # enable matplotlib integration
ipython --matplotlib=qt # enable matplotlib integration with qt4 backend
ipython --log-level=DEBUG # set logging to DEBUG
ipython --profile=foo # start with profile foo
ipython profile create foo # create profile foo w/ default config files
ipython help profile # show the help for the profile subcmd
ipython locate # print the path to the IPython directory
ipython locate profile foo # print the path to the directory for profile `foo`
error log
!ENTRY com.aptana.shared_core 4 4 2018-12-22 11:43:01.037
!MESSAGE Unable to recreate the Interpreter info (Its format changed. Please, re-create your Interpreter information).Contents found:=========
IPython
=========
Tools for Interactive Computing in Python
=========================================
A Python shell with automatic history (input and output), dynamic object
introspection, easier configuration, command completion, access to the
system shell and more. IPython can also be embedded in running programs.
Usage
ipython [subcommand] [options] [-c cmd | -m mod | file] [--] [arg] ...
If invoked with no options, it executes the file and exits, passing the
remaining arguments to the script, just as if you had specified the same
command with python. You may need to specify `--` before args to be passed
to the script, to prevent IPython from attempting to parse them. If you
specify the option `-i` before the filename, it will enter an interactive
IPython session after running the script, rather than exiting. Files ending
in .py will be treated as normal Python, but files ending in .ipy can
contain special IPython syntax (magic commands, shell expansions, etc.).
Almost all configuration in IPython is available via the command-line. Do
`ipython --help-all` to see all available options. For persistent
configuration, look into your `ipython_config.py` configuration file for
details.
This file is typically installed in the `IPYTHONDIR` directory, and there
is a separate configuration directory for each profile. The default profile
directory will be located in $IPYTHONDIR/profile_default. IPYTHONDIR
defaults to to `$HOME/.ipython`. For Windows users, $HOME resolves to
C:\Users\YourUserName in most instances.
To initialize a profile with the default configuration file, do::
$> ipython profile create
and start editing `IPYTHONDIR/profile_default/ipython_config.py`
In IPython's documentation, we will refer to this directory as
`IPYTHONDIR`, you can change its default location by creating an
environment variable with this name and setting it to the desired path.
For more information, see the manual available in HTML and PDF in your
installation, or online at http://ipython.org/documentation.html.
Subcommands
-----------
Subcommands are launched as `ipython cmd [args]`. For information on using
subcommand 'cmd', do: `ipython cmd -h`.
profile
Create and manage IPython profiles.
kernel
Start a kernel without an attached frontend.
locate
print the path to the IPython dir
history
Manage the IPython history database.
qtconsole
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Launch the Jupyter Qt Console.
notebook
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Launch the Jupyter HTML Notebook Server.
console
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Launch the Jupyter terminal-based Console.
nbconvert
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Convert notebooks to/from other formats.
trust
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Sign notebooks to trust their potentially unsafe contents at load.
kernelspec
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Manage Jupyter kernel specifications.
install-nbextension
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Install Jupyter notebook extension files
Options
-------
Arguments that take values are actually convenience aliases to full
Configurables, whose aliases are listed on the help line. For more information
on full configurables, see '--help-all'.
--debug
set log level to logging.DEBUG (maximize logging output)
--quiet
set log level to logging.CRITICAL (minimize logging output)
--init
Initialize profile with default config files. This is equivalent
to running `ipython profile create <profile>` prior to startup.
--autoindent
Turn on autoindenting.
--no-autoindent
Turn off autoindenting.
--automagic
Turn on the auto calling of magic commands. Type %%magic at the
IPython prompt for more information.
--no-automagic
Turn off the auto calling of magic commands.
--pdb
Enable auto calling the pdb debugger after every exception.
--no-pdb
Disable auto calling the pdb debugger after every exception.
--pprint
Enable auto pretty printing of results.
--no-pprint
Disable auto pretty printing of results.
--color-info
IPython can display information about objects via a set of functions,
and optionally can use colors for this, syntax highlighting
source code and various other elements. This is on by default, but can cause
problems with some pagers. If you see such problems, you can disable the
colours.
--no-color-info
Disable using colors for info related things.
--nosep
Eliminate all spacing between prompts.
--pylab
Pre-load matplotlib and numpy for interactive use with
the default matplotlib backend.
--matplotlib
Configure matplotlib for interactive use with
the default matplotlib backend.
--autoedit-syntax
Turn on auto editing of files with syntax errors.
--no-autoedit-syntax
Turn off auto editing of files with syntax errors.
--simple-prompt
Force simple minimal prompt using `raw_input`
--no-simple-prompt
Use a rich interactive prompt with prompt_toolkit
--banner
Display a banner upon starting IPython.
--no-banner
Don't display a banner upon starting IPython.
--confirm-exit
Set to confirm when you try to exit IPython with an EOF (Control-D
in Unix, Control-Z/Enter in Windows). By typing 'exit' or 'quit',
you can force a direct exit without any confirmation.
--no-confirm-exit
Don't prompt the user when exiting.
--term-title
Enable auto setting the terminal title.
--no-term-title
Disable auto setting the terminal title.
--classic
Gives IPython a similar feel to the classic Python prompt.
--quick
Enable quick startup with no config files.
-i
If running code from the command line, become interactive afterwards.
It is often useful to follow this with `--` to treat remaining flags as
script arguments.
--profile-dir=<Unicode> (ProfileDir.location)
Default: ''
Set the profile location directly. This overrides the logic used by the
`profile` option.
--profile=<Unicode> (BaseIPythonApplication.profile)
Default: 'default'
The IPython profile to use.
--ipython-dir=<Unicode> (BaseIPythonApplication.ipython_dir)
Default: ''
The name of the IPython directory. This directory is used for logging
configuration (through profiles), history storage, etc. The default is
usually $HOME/.ipython. This option can also be specified through the
environment variable IPYTHONDIR.
--log-level=<Enum> (Application.log_level)
Default: 30
Choices: (0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 'DEBUG', 'INFO', 'WARN', 'ERROR', 'CRITICAL')
Set the log level by value or name.
--config=<Unicode> (BaseIPythonApplication.extra_config_file)
Default: ''
Path to an extra config file to load.
If specified, load this config file in addition to any other IPython config.
--autocall=<Enum> (InteractiveShell.autocall)
Default: 0
Choices: (0, 1, 2)
Make IPython automatically call any callable object even if you didn't type
explicit parentheses. For example, 'str 43' becomes 'str(43)' automatically.
The value can be '0' to disable the feature, '1' for 'smart' autocall, where
it is not applied if there are no more arguments on the line, and '2' for
'full' autocall, where all callable objects are automatically called (even
if no arguments are present).
--colors=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShell.colors)
Default: 'Neutral'
Choices: ['Neutral', 'NoColor', 'LightBG', 'Linux']
Set the color scheme (NoColor, Neutral, Linux, or LightBG).
--logfile=<Unicode> (InteractiveShell.logfile)
Default: ''
The name of the logfile to use.
--logappend=<Unicode> (InteractiveShell.logappend)
Default: ''
Start logging to the given file in append mode. Use `logfile` to specify a
log file to **overwrite** logs to.
-c <Unicode> (InteractiveShellApp.code_to_run)
Default: ''
Execute the given command string.
-m <Unicode> (InteractiveShellApp.module_to_run)
Default: ''
Run the module as a script.
--ext=<Unicode> (InteractiveShellApp.extra_extension)
Default: ''
dotted module name of an IPython extension to load.
--gui=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShellApp.gui)
Default: None
Choices: ['glut', 'gtk', 'gtk2', 'gtk3', 'osx', 'pyglet', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'wx', 'gtk2', 'qt4']
Enable GUI event loop integration with any of ('glut', 'gtk', 'gtk2',
'gtk3', 'osx', 'pyglet', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'wx', 'gtk2', 'qt4').
--pylab=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShellApp.pylab)
Default: None
Choices: ['auto', 'agg', 'gtk', 'gtk3', 'inline', 'ipympl', 'nbagg', 'notebook', 'osx', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'widget', 'wx']
Pre-load matplotlib and numpy for interactive use, selecting a particular
matplotlib backend and loop integration.
--matplotlib=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShellApp.matplotlib)
Default: None
Choices: ['auto', 'agg', 'gtk', 'gtk3', 'inline', 'ipympl', 'nbagg', 'notebook', 'osx', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'widget', 'wx']
Configure matplotlib for interactive use with the default matplotlib
backend.
--cache-size=<Int> (InteractiveShell.cache_size)
Default: 1000
Set the size of the output cache. The default is 1000, you can change it
permanently in your config file. Setting it to 0 completely disables the
caching system, and the minimum value accepted is 3 (if you provide a value
less than 3, it is reset to 0 and a warning is issued). This limit is
defined because otherwise you'll spend more time re-flushing a too small
cache than working
To see all available configurables, use `--help-all`
Examples
--------
ipython --matplotlib # enable matplotlib integration
ipython --matplotlib=qt # enable matplotlib integration with qt4 backend
ipython --log-level=DEBUG # set logging to DEBUG
ipython --profile=foo # start with profile foo
ipython profile create foo # create profile foo w/ default config files
ipython help profile # show the help for the profile subcmd
ipython locate # print the path to the IPython directory
ipython locate profile foo # print the path to the directory for profile `foo`
!STACK 0
java.lang.RuntimeException: Unable to recreate the Interpreter info (Its format changed. Please, re-create your Interpreter information).Contents found:=========
IPython
=========
Tools for Interactive Computing in Python
=========================================
A Python shell with automatic history (input and output), dynamic object
introspection, easier configuration, command completion, access to the
system shell and more. IPython can also be embedded in running programs.
Usage
ipython [subcommand] [options] [-c cmd | -m mod | file] [--] [arg] ...
If invoked with no options, it executes the file and exits, passing the
remaining arguments to the script, just as if you had specified the same
command with python. You may need to specify `--` before args to be passed
to the script, to prevent IPython from attempting to parse them. If you
specify the option `-i` before the filename, it will enter an interactive
IPython session after running the script, rather than exiting. Files ending
in .py will be treated as normal Python, but files ending in .ipy can
contain special IPython syntax (magic commands, shell expansions, etc.).
Almost all configuration in IPython is available via the command-line. Do
`ipython --help-all` to see all available options. For persistent
configuration, look into your `ipython_config.py` configuration file for
details.
This file is typically installed in the `IPYTHONDIR` directory, and there
is a separate configuration directory for each profile. The default profile
directory will be located in $IPYTHONDIR/profile_default. IPYTHONDIR
defaults to to `$HOME/.ipython`. For Windows users, $HOME resolves to
C:\Users\YourUserName in most instances.
To initialize a profile with the default configuration file, do::
$> ipython profile create
and start editing `IPYTHONDIR/profile_default/ipython_config.py`
In IPython's documentation, we will refer to this directory as
`IPYTHONDIR`, you can change its default location by creating an
environment variable with this name and setting it to the desired path.
For more information, see the manual available in HTML and PDF in your
installation, or online at http://ipython.org/documentation.html.
Subcommands
-----------
Subcommands are launched as `ipython cmd [args]`. For information on using
subcommand 'cmd', do: `ipython cmd -h`.
profile
Create and manage IPython profiles.
kernel
Start a kernel without an attached frontend.
locate
print the path to the IPython dir
history
Manage the IPython history database.
qtconsole
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Launch the Jupyter Qt Console.
notebook
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Launch the Jupyter HTML Notebook Server.
console
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Launch the Jupyter terminal-based Console.
nbconvert
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Convert notebooks to/from other formats.
trust
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Sign notebooks to trust their potentially unsafe contents at load.
kernelspec
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Manage Jupyter kernel specifications.
install-nbextension
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Install Jupyter notebook extension files
Options
-------
Arguments that take values are actually convenience aliases to full
Configurables, whose aliases are listed on the help line. For more information
on full configurables, see '--help-all'.
--debug
set log level to logging.DEBUG (maximize logging output)
--quiet
set log level to logging.CRITICAL (minimize logging output)
--init
Initialize profile with default config files. This is equivalent
to running `ipython profile create <profile>` prior to startup.
--autoindent
Turn on autoindenting.
--no-autoindent
Turn off autoindenting.
--automagic
Turn on the auto calling of magic commands. Type %%magic at the
IPython prompt for more information.
--no-automagic
Turn off the auto calling of magic commands.
--pdb
Enable auto calling the pdb debugger after every exception.
--no-pdb
Disable auto calling the pdb debugger after every exception.
--pprint
Enable auto pretty printing of results.
--no-pprint
Disable auto pretty printing of results.
--color-info
IPython can display information about objects via a set of functions,
and optionally can use colors for this, syntax highlighting
source code and various other elements. This is on by default, but can cause
problems with some pagers. If you see such problems, you can disable the
colours.
--no-color-info
Disable using colors for info related things.
--nosep
Eliminate all spacing between prompts.
--pylab
Pre-load matplotlib and numpy for interactive use with
the default matplotlib backend.
--matplotlib
Configure matplotlib for interactive use with
the default matplotlib backend.
--autoedit-syntax
Turn on auto editing of files with syntax errors.
--no-autoedit-syntax
Turn off auto editing of files with syntax errors.
--simple-prompt
Force simple minimal prompt using `raw_input`
--no-simple-prompt
Use a rich interactive prompt with prompt_toolkit
--banner
Display a banner upon starting IPython.
--no-banner
Don't display a banner upon starting IPython.
--confirm-exit
Set to confirm when you try to exit IPython with an EOF (Control-D
in Unix, Control-Z/Enter in Windows). By typing 'exit' or 'quit',
you can force a direct exit without any confirmation.
--no-confirm-exit
Don't prompt the user when exiting.
--term-title
Enable auto setting the terminal title.
--no-term-title
Disable auto setting the terminal title.
--classic
Gives IPython a similar feel to the classic Python prompt.
--quick
Enable quick startup with no config files.
-i
If running code from the command line, become interactive afterwards.
It is often useful to follow this with `--` to treat remaining flags as
script arguments.
--profile-dir=<Unicode> (ProfileDir.location)
Default: ''
Set the profile location directly. This overrides the logic used by the
`profile` option.
--profile=<Unicode> (BaseIPythonApplication.profile)
Default: 'default'
The IPython profile to use.
--ipython-dir=<Unicode> (BaseIPythonApplication.ipython_dir)
Default: ''
The name of the IPython directory. This directory is used for logging
configuration (through profiles), history storage, etc. The default is
usually $HOME/.ipython. This option can also be specified through the
environment variable IPYTHONDIR.
--log-level=<Enum> (Application.log_level)
Default: 30
Choices: (0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 'DEBUG', 'INFO', 'WARN', 'ERROR', 'CRITICAL')
Set the log level by value or name.
--config=<Unicode> (BaseIPythonApplication.extra_config_file)
Default: ''
Path to an extra config file to load.
If specified, load this config file in addition to any other IPython config.
--autocall=<Enum> (InteractiveShell.autocall)
Default: 0
Choices: (0, 1, 2)
Make IPython automatically call any callable object even if you didn't type
explicit parentheses. For example, 'str 43' becomes 'str(43)' automatically.
The value can be '0' to disable the feature, '1' for 'smart' autocall, where
it is not applied if there are no more arguments on the line, and '2' for
'full' autocall, where all callable objects are automatically called (even
if no arguments are present).
--colors=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShell.colors)
Default: 'Neutral'
Choices: ['Neutral', 'NoColor', 'LightBG', 'Linux']
Set the color scheme (NoColor, Neutral, Linux, or LightBG).
--logfile=<Unicode> (InteractiveShell.logfile)
Default: ''
The name of the logfile to use.
--logappend=<Unicode> (InteractiveShell.logappend)
Default: ''
Start logging to the given file in append mode. Use `logfile` to specify a
log file to **overwrite** logs to.
-c <Unicode> (InteractiveShellApp.code_to_run)
Default: ''
Execute the given command string.
-m <Unicode> (InteractiveShellApp.module_to_run)
Default: ''
Run the module as a script.
--ext=<Unicode> (InteractiveShellApp.extra_extension)
Default: ''
dotted module name of an IPython extension to load.
--gui=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShellApp.gui)
Default: None
Choices: ['glut', 'gtk', 'gtk2', 'gtk3', 'osx', 'pyglet', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'wx', 'gtk2', 'qt4']
Enable GUI event loop integration with any of ('glut', 'gtk', 'gtk2',
'gtk3', 'osx', 'pyglet', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'wx', 'gtk2', 'qt4').
--pylab=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShellApp.pylab)
Default: None
Choices: ['auto', 'agg', 'gtk', 'gtk3', 'inline', 'ipympl', 'nbagg', 'notebook', 'osx', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'widget', 'wx']
Pre-load matplotlib and numpy for interactive use, selecting a particular
matplotlib backend and loop integration.
--matplotlib=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShellApp.matplotlib)
Default: None
Choices: ['auto', 'agg', 'gtk', 'gtk3', 'inline', 'ipympl', 'nbagg', 'notebook', 'osx', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'widget', 'wx']
Configure matplotlib for interactive use with the default matplotlib
backend.
--cache-size=<Int> (InteractiveShell.cache_size)
Default: 1000
Set the size of the output cache. The default is 1000, you can change it
permanently in your config file. Setting it to 0 completely disables the
caching system, and the minimum value accepted is 3 (if you provide a value
less than 3, it is reset to 0 and a warning is issued). This limit is
defined because otherwise you'll spend more time re-flushing a too small
cache than working
To see all available configurables, use `--help-all`
Examples
--------
ipython --matplotlib # enable matplotlib integration
ipython --matplotlib=qt # enable matplotlib integration with qt4 backend
ipython --log-level=DEBUG # set logging to DEBUG
ipython --profile=foo # start with profile foo
ipython profile create foo # create profile foo w/ default config files
ipython help profile # show the help for the profile subcmd
ipython locate # print the path to the IPython directory
ipython locate profile foo # print the path to the directory for profile `foo`
at org.python.pydev.ui.pythonpathconf.InterpreterInfo.fromString(InterpreterInfo.java:287)
at org.python.pydev.ui.interpreters.AbstractInterpreterManager.createInfoFromOutput(AbstractInterpreterManager.java:422)
at org.python.pydev.ui.interpreters.PythonInterpreterManager.doCreateInterpreterInfo(PythonInterpreterManager.java:72)
at org.python.pydev.ui.interpreters.PythonInterpreterManager.internalCreateInterpreterInfo(PythonInterpreterManager.java:45)
at org.python.pydev.ui.interpreters.AbstractInterpreterManager.createInterpreterInfo(AbstractInterpreterManager.java:369)
at org.python.pydev.ui.pythonpathconf.ObtainInterpreterInfoOperation.run(ObtainInterpreterInfoOperation.java:78)
at org.eclipse.jface.operation.ModalContext$ModalContextThread.run(ModalContext.java:121)
!ENTRY com.aptana.shared_core 1 1 2018-12-22 11:43:03.935
!MESSAGE Information about process of adding new interpreter:
- Opening dialog to request executable (or jar).
- Chosen interpreter (name and file):'Tuple [ipy -- C:\Program Files\Python36\Scripts\ipython.exe]
- Ok, file is non-null. Getting info on:C:\Program Files\Python36\Scripts\ipython.exe
- Beggining task:Getting libs totalWork:100
- Setting task name:Mounting executable string...
- Setting task name:Executing: "C:\Program Files\Python36\Scripts\ipython.exe" -u "C:\Users\devlapt\AppData\Local\Aptana Studio 3\plugins\org.python.pydev_2.7.0.2013032300\pysrc\interpreterInfo.py"
- Setting task name:Making pythonpath environment... "C:\Program Files\Python36\Scripts\ipython.exe" -u "C:\Users\devlapt\AppData\Local\Aptana Studio 3\plugins\org.python.pydev_2.7.0.2013032300\pysrc\interpreterInfo.py"
- Setting task name:Making exec... "C:\Program Files\Python36\Scripts\ipython.exe" -u "C:\Users\devlapt\AppData\Local\Aptana Studio 3\plugins\org.python.pydev_2.7.0.2013032300\pysrc\interpreterInfo.py"
- Setting task name:Reading output...
- Setting task name:Waiting for process to finish.
Exception detected: Unable to recreate the Interpreter info (Its format changed. Please, re-create your Interpreter information).Contents found:=========
IPython
=========
Tools for Interactive Computing in Python
=========================================
A Python shell with automatic history (input and output), dynamic object
introspection, easier configuration, command completion, access to the
system shell and more. IPython can also be embedded in running programs.
Usage
ipython [subcommand] [options] [-c cmd | -m mod | file] [--] [arg] ...
If invoked with no options, it executes the file and exits, passing the
remaining arguments to the script, just as if you had specified the same
command with python. You may need to specify `--` before args to be passed
to the script, to prevent IPython from attempting to parse them. If you
specify the option `-i` before the filename, it will enter an interactive
IPython session after running the script, rather than exiting. Files ending
in .py will be treated as normal Python, but files ending in .ipy can
contain special IPython syntax (magic commands, shell expansions, etc.).
Almost all configuration in IPython is available via the command-line. Do
`ipython --help-all` to see all available options. For persistent
configuration, look into your `ipython_config.py` configuration file for
details.
This file is typically installed in the `IPYTHONDIR` directory, and there
is a separate configuration directory for each profile. The default profile
directory will be located in $IPYTHONDIR/profile_default. IPYTHONDIR
defaults to to `$HOME/.ipython`. For Windows users, $HOME resolves to
C:\Users\YourUserName in most instances.
To initialize a profile with the default configuration file, do::
$> ipython profile create
and start editing `IPYTHONDIR/profile_default/ipython_config.py`
In IPython's documentation, we will refer to this directory as
`IPYTHONDIR`, you can change its default location by creating an
environment variable with this name and setting it to the desired path.
For more information, see the manual available in HTML and PDF in your
installation, or online at http://ipython.org/documentation.html.
Subcommands
-----------
Subcommands are launched as `ipython cmd [args]`. For information on using
subcommand 'cmd', do: `ipython cmd -h`.
profile
Create and manage IPython profiles.
kernel
Start a kernel without an attached frontend.
locate
print the path to the IPython dir
history
Manage the IPython history database.
qtconsole
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Launch the Jupyter Qt Console.
notebook
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Launch the Jupyter HTML Notebook Server.
console
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Launch the Jupyter terminal-based Console.
nbconvert
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Convert notebooks to/from other formats.
trust
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Sign notebooks to trust their potentially unsafe contents at load.
kernelspec
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Manage Jupyter kernel specifications.
install-nbextension
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Install Jupyter notebook extension files
Options
-------
Arguments that take values are actually convenience aliases to full
Configurables, whose aliases are listed on the help line. For more information
on full configurables, see '--help-all'.
--debug
set log level to logging.DEBUG (maximize logging output)
--quiet
set log level to logging.CRITICAL (minimize logging output)
--init
Initialize profile with default config files. This is equivalent
to running `ipython profile create <profile>` prior to startup.
--autoindent
Turn on autoindenting.
--no-autoindent
Turn off autoindenting.
--automagic
Turn on the auto calling of magic commands. Type %%magic at the
IPython prompt for more information.
--no-automagic
Turn off the auto calling of magic commands.
--pdb
Enable auto calling the pdb debugger after every exception.
--no-pdb
Disable auto calling the pdb debugger after every exception.
--pprint
Enable auto pretty printing of results.
--no-pprint
Disable auto pretty printing of results.
--color-info
IPython can display information about objects via a set of functions,
and optionally can use colors for this, syntax highlighting
source code and various other elements. This is on by default, but can cause
problems with some pagers. If you see such problems, you can disable the
colours.
--no-color-info
Disable using colors for info related things.
--nosep
Eliminate all spacing between prompts.
--pylab
Pre-load matplotlib and numpy for interactive use with
the default matplotlib backend.
--matplotlib
Configure matplotlib for interactive use with
the default matplotlib backend.
--autoedit-syntax
Turn on auto editing of files with syntax errors.
--no-autoedit-syntax
Turn off auto editing of files with syntax errors.
--simple-prompt
Force simple minimal prompt using `raw_input`
--no-simple-prompt
Use a rich interactive prompt with prompt_toolkit
--banner
Display a banner upon starting IPython.
--no-banner
Don't display a banner upon starting IPython.
--confirm-exit
Set to confirm when you try to exit IPython with an EOF (Control-D
in Unix, Control-Z/Enter in Windows). By typing 'exit' or 'quit',
you can force a direct exit without any confirmation.
--no-confirm-exit
Don't prompt the user when exiting.
--term-title
Enable auto setting the terminal title.
--no-term-title
Disable auto setting the terminal title.
--classic
Gives IPython a similar feel to the classic Python prompt.
--quick
Enable quick startup with no config files.
-i
If running code from the command line, become interactive afterwards.
It is often useful to follow this with `--` to treat remaining flags as
script arguments.
--profile-dir=<Unicode> (ProfileDir.location)
Default: ''
Set the profile location directly. This overrides the logic used by the
`profile` option.
--profile=<Unicode> (BaseIPythonApplication.profile)
Default: 'default'
The IPython profile to use.
--ipython-dir=<Unicode> (BaseIPythonApplication.ipython_dir)
Default: ''
The name of the IPython directory. This directory is used for logging
configuration (through profiles), history storage, etc. The default is
usually $HOME/.ipython. This option can also be specified through the
environment variable IPYTHONDIR.
--log-level=<Enum> (Application.log_level)
Default: 30
Choices: (0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 'DEBUG', 'INFO', 'WARN', 'ERROR', 'CRITICAL')
Set the log level by value or name.
--config=<Unicode> (BaseIPythonApplication.extra_config_file)
Default: ''
Path to an extra config file to load.
If specified, load this config file in addition to any other IPython config.
--autocall=<Enum> (InteractiveShell.autocall)
Default: 0
Choices: (0, 1, 2)
Make IPython automatically call any callable object even if you didn't type
explicit parentheses. For example, 'str 43' becomes 'str(43)' automatically.
The value can be '0' to disable the feature, '1' for 'smart' autocall, where
it is not applied if there are no more arguments on the line, and '2' for
'full' autocall, where all callable objects are automatically called (even
if no arguments are present).
--colors=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShell.colors)
Default: 'Neutral'
Choices: ['Neutral', 'NoColor', 'LightBG', 'Linux']
Set the color scheme (NoColor, Neutral, Linux, or LightBG).
--logfile=<Unicode> (InteractiveShell.logfile)
Default: ''
The name of the logfile to use.
--logappend=<Unicode> (InteractiveShell.logappend)
Default: ''
Start logging to the given file in append mode. Use `logfile` to specify a
log file to **overwrite** logs to.
-c <Unicode> (InteractiveShellApp.code_to_run)
Default: ''
Execute the given command string.
-m <Unicode> (InteractiveShellApp.module_to_run)
Default: ''
Run the module as a script.
--ext=<Unicode> (InteractiveShellApp.extra_extension)
Default: ''
dotted module name of an IPython extension to load.
--gui=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShellApp.gui)
Default: None
Choices: ['glut', 'gtk', 'gtk2', 'gtk3', 'osx', 'pyglet', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'wx', 'gtk2', 'qt4']
Enable GUI event loop integration with any of ('glut', 'gtk', 'gtk2',
'gtk3', 'osx', 'pyglet', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'wx', 'gtk2', 'qt4').
--pylab=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShellApp.pylab)
Default: None
Choices: ['auto', 'agg', 'gtk', 'gtk3', 'inline', 'ipympl', 'nbagg', 'notebook', 'osx', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'widget', 'wx']
Pre-load matplotlib and numpy for interactive use, selecting a particular
matplotlib backend and loop integration.
--matplotlib=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShellApp.matplotlib)
Default: None
Choices: ['auto', 'agg', 'gtk', 'gtk3', 'inline', 'ipympl', 'nbagg', 'notebook', 'osx', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'widget', 'wx']
Configure matplotlib for interactive use with the default matplotlib
backend.
--cache-size=<Int> (InteractiveShell.cache_size)
Default: 1000
Set the size of the output cache. The default is 1000, you can change it
permanently in your config file. Setting it to 0 completely disables the
caching system, and the minimum value accepted is 3 (if you provide a value
less than 3, it is reset to 0 and a warning is issued). This limit is
defined because otherwise you'll spend more time re-flushing a too small
cache than working
To see all available configurables, use `--help-all`
Examples
--------
ipython --matplotlib # enable matplotlib integration
ipython --matplotlib=qt # enable matplotlib integration with qt4 backend
ipython --log-level=DEBUG # set logging to DEBUG
ipython --profile=foo # start with profile foo
ipython profile create foo # create profile foo w/ default config files
ipython help profile # show the help for the profile subcmd
ipython locate # print the path to the IPython directory
ipython locate profile foo # print the path to the directory for profile `foo`
- Some error happened while getting info on the interpreter:
java.lang.RuntimeException: Unable to recreate the Interpreter info (Its format changed. Please, re-create your Interpreter information).Contents found:=========
IPython
=========
Tools for Interactive Computing in Python
=========================================
A Python shell with automatic history (input and output), dynamic object
introspection, easier configuration, command completion, access to the
system shell and more. IPython can also be embedded in running programs.
Usage
ipython [subcommand] [options] [-c cmd | -m mod | file] [--] [arg] ...
If invoked with no options, it executes the file and exits, passing the
remaining arguments to the script, just as if you had specified the same
command with python. You may need to specify `--` before args to be passed
to the script, to prevent IPython from attempting to parse them. If you
specify the option `-i` before the filename, it will enter an interactive
IPython session after running the script, rather than exiting. Files ending
in .py will be treated as normal Python, but files ending in .ipy can
contain special IPython syntax (magic commands, shell expansions, etc.).
Almost all configuration in IPython is available via the command-line. Do
`ipython --help-all` to see all available options. For persistent
configuration, look into your `ipython_config.py` configuration file for
details.
This file is typically installed in the `IPYTHONDIR` directory, and there
is a separate configuration directory for each profile. The default profile
directory will be located in $IPYTHONDIR/profile_default. IPYTHONDIR
defaults to to `$HOME/.ipython`. For Windows users, $HOME resolves to
C:\Users\YourUserName in most instances.
To initialize a profile with the default configuration file, do::
$> ipython profile create
and start editing `IPYTHONDIR/profile_default/ipython_config.py`
In IPython's documentation, we will refer to this directory as
`IPYTHONDIR`, you can change its default location by creating an
environment variable with this name and setting it to the desired path.
For more information, see the manual available in HTML and PDF in your
installation, or online at http://ipython.org/documentation.html.
Subcommands
-----------
Subcommands are launched as `ipython cmd [args]`. For information on using
subcommand 'cmd', do: `ipython cmd -h`.
profile
Create and manage IPython profiles.
kernel
Start a kernel without an attached frontend.
locate
print the path to the IPython dir
history
Manage the IPython history database.
qtconsole
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Launch the Jupyter Qt Console.
notebook
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Launch the Jupyter HTML Notebook Server.
console
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Launch the Jupyter terminal-based Console.
nbconvert
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Convert notebooks to/from other formats.
trust
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Sign notebooks to trust their potentially unsafe contents at load.
kernelspec
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Manage Jupyter kernel specifications.
install-nbextension
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Install Jupyter notebook extension files
Options
-------
Arguments that take values are actually convenience aliases to full
Configurables, whose aliases are listed on the help line. For more information
on full configurables, see '--help-all'.
--debug
set log level to logging.DEBUG (maximize logging output)
--quiet
set log level to logging.CRITICAL (minimize logging output)
--init
Initialize profile with default config files. This is equivalent
to running `ipython profile create <profile>` prior to startup.
--autoindent
Turn on autoindenting.
--no-autoindent
Turn off autoindenting.
--automagic
Turn on the auto calling of magic commands. Type %%magic at the
IPython prompt for more information.
--no-automagic
Turn off the auto calling of magic commands.
--pdb
Enable auto calling the pdb debugger after every exception.
--no-pdb
Disable auto calling the pdb debugger after every exception.
--pprint
Enable auto pretty printing of results.
--no-pprint
Disable auto pretty printing of results.
--color-info
IPython can display information about objects via a set of functions,
and optionally can use colors for this, syntax highlighting
source code and various other elements. This is on by default, but can cause
problems with some pagers. If you see such problems, you can disable the
colours.
--no-color-info
Disable using colors for info related things.
--nosep
Eliminate all spacing between prompts.
--pylab
Pre-load matplotlib and numpy for interactive use with
the default matplotlib backend.
--matplotlib
Configure matplotlib for interactive use with
the default matplotlib backend.
--autoedit-syntax
Turn on auto editing of files with syntax errors.
--no-autoedit-syntax
Turn off auto editing of files with syntax errors.
--simple-prompt
Force simple minimal prompt using `raw_input`
--no-simple-prompt
Use a rich interactive prompt with prompt_toolkit
--banner
Display a banner upon starting IPython.
--no-banner
Don't display a banner upon starting IPython.
--confirm-exit
Set to confirm when you try to exit IPython with an EOF (Control-D
in Unix, Control-Z/Enter in Windows). By typing 'exit' or 'quit',
you can force a direct exit without any confirmation.
--no-confirm-exit
Don't prompt the user when exiting.
--term-title
Enable auto setting the terminal title.
--no-term-title
Disable auto setting the terminal title.
--classic
Gives IPython a similar feel to the classic Python prompt.
--quick
Enable quick startup with no config files.
-i
If running code from the command line, become interactive afterwards.
It is often useful to follow this with `--` to treat remaining flags as
script arguments.
--profile-dir=<Unicode> (ProfileDir.location)
Default: ''
Set the profile location directly. This overrides the logic used by the
`profile` option.
--profile=<Unicode> (BaseIPythonApplication.profile)
Default: 'default'
The IPython profile to use.
--ipython-dir=<Unicode> (BaseIPythonApplication.ipython_dir)
Default: ''
The name of the IPython directory. This directory is used for logging
configuration (through profiles), history storage, etc. The default is
usually $HOME/.ipython. This option can also be specified through the
environment variable IPYTHONDIR.
--log-level=<Enum> (Application.log_level)
Default: 30
Choices: (0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 'DEBUG', 'INFO', 'WARN', 'ERROR', 'CRITICAL')
Set the log level by value or name.
--config=<Unicode> (BaseIPythonApplication.extra_config_file)
Default: ''
Path to an extra config file to load.
If specified, load this config file in addition to any other IPython config.
--autocall=<Enum> (InteractiveShell.autocall)
Default: 0
Choices: (0, 1, 2)
Make IPython automatically call any callable object even if you didn't type
explicit parentheses. For example, 'str 43' becomes 'str(43)' automatically.
The value can be '0' to disable the feature, '1' for 'smart' autocall, where
it is not applied if there are no more arguments on the line, and '2' for
'full' autocall, where all callable objects are automatically called (even
if no arguments are present).
--colors=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShell.colors)
Default: 'Neutral'
Choices: ['Neutral', 'NoColor', 'LightBG', 'Linux']
Set the color scheme (NoColor, Neutral, Linux, or LightBG).
--logfile=<Unicode> (InteractiveShell.logfile)
Default: ''
The name of the logfile to use.
--logappend=<Unicode> (InteractiveShell.logappend)
Default: ''
Start logging to the given file in append mode. Use `logfile` to specify a
log file to **overwrite** logs to.
-c <Unicode> (InteractiveShellApp.code_to_run)
Default: ''
Execute the given command string.
-m <Unicode> (InteractiveShellApp.module_to_run)
Default: ''
Run the module as a script.
--ext=<Unicode> (InteractiveShellApp.extra_extension)
Default: ''
dotted module name of an IPython extension to load.
--gui=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShellApp.gui)
Default: None
Choices: ['glut', 'gtk', 'gtk2', 'gtk3', 'osx', 'pyglet', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'wx', 'gtk2', 'qt4']
Enable GUI event loop integration with any of ('glut', 'gtk', 'gtk2',
'gtk3', 'osx', 'pyglet', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'wx', 'gtk2', 'qt4').
--pylab=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShellApp.pylab)
Default: None
Choices: ['auto', 'agg', 'gtk', 'gtk3', 'inline', 'ipympl', 'nbagg', 'notebook', 'osx', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'widget', 'wx']
Pre-load matplotlib and numpy for interactive use, selecting a particular
matplotlib backend and loop integration.
--matplotlib=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShellApp.matplotlib)
Default: None
Choices: ['auto', 'agg', 'gtk', 'gtk3', 'inline', 'ipympl', 'nbagg', 'notebook', 'osx', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'widget', 'wx']
Configure matplotlib for interactive use with the default matplotlib
backend.
--cache-size=<Int> (InteractiveShell.cache_size)
Default: 1000
Set the size of the output cache. The default is 1000, you can change it
permanently in your config file. Setting it to 0 completely disables the
caching system, and the minimum value accepted is 3 (if you provide a value
less than 3, it is reset to 0 and a warning is issued). This limit is
defined because otherwise you'll spend more time re-flushing a too small
cache than working
To see all available configurables, use `--help-all`
Examples
--------
ipython --matplotlib # enable matplotlib integration
ipython --matplotlib=qt # enable matplotlib integration with qt4 backend
ipython --log-level=DEBUG # set logging to DEBUG
ipython --profile=foo # start with profile foo
ipython profile create foo # create profile foo w/ default config files
ipython help profile # show the help for the profile subcmd
ipython locate # print the path to the IPython directory
ipython locate profile foo # print the path to the directory for profile `foo`
at org.python.pydev.ui.pythonpathconf.InterpreterInfo.fromString(InterpreterInfo.java:287)
at org.python.pydev.ui.interpreters.AbstractInterpreterManager.createInfoFromOutput(AbstractInterpreterManager.java:422)
at org.python.pydev.ui.interpreters.PythonInterpreterManager.doCreateInterpreterInfo(PythonInterpreterManager.java:72)
at org.python.pydev.ui.interpreters.PythonInterpreterManager.internalCreateInterpreterInfo(PythonInterpreterManager.java:45)
at org.python.pydev.ui.interpreters.AbstractInterpreterManager.createInterpreterInfo(AbstractInterpreterManager.java:369)
at org.python.pydev.ui.pythonpathconf.ObtainInterpreterInfoOperation.run(ObtainInterpreterInfoOperation.java:78)
at org.eclipse.jface.operation.ModalContext$ModalContextThread.run(ModalContext.java:121)
!STACK 0
java.lang.RuntimeException: Information about process of adding new interpreter:
- Opening dialog to request executable (or jar).
- Chosen interpreter (name and file):'Tuple [ipy -- C:\Program Files\Python36\Scripts\ipython.exe]
- Ok, file is non-null. Getting info on:C:\Program Files\Python36\Scripts\ipython.exe
- Beggining task:Getting libs totalWork:100
- Setting task name:Mounting executable string...
- Setting task name:Executing: "C:\Program Files\Python36\Scripts\ipython.exe" -u "C:\Users\devlapt\AppData\Local\Aptana Studio 3\plugins\org.python.pydev_2.7.0.2013032300\pysrc\interpreterInfo.py"
- Setting task name:Making pythonpath environment... "C:\Program Files\Python36\Scripts\ipython.exe" -u "C:\Users\devlapt\AppData\Local\Aptana Studio 3\plugins\org.python.pydev_2.7.0.2013032300\pysrc\interpreterInfo.py"
- Setting task name:Making exec... "C:\Program Files\Python36\Scripts\ipython.exe" -u "C:\Users\devlapt\AppData\Local\Aptana Studio 3\plugins\org.python.pydev_2.7.0.2013032300\pysrc\interpreterInfo.py"
- Setting task name:Reading output...
- Setting task name:Waiting for process to finish.
Exception detected: Unable to recreate the Interpreter info (Its format changed. Please, re-create your Interpreter information).Contents found:=========
IPython
=========
Tools for Interactive Computing in Python
=========================================
A Python shell with automatic history (input and output), dynamic object
introspection, easier configuration, command completion, access to the
system shell and more. IPython can also be embedded in running programs.
Usage
ipython [subcommand] [options] [-c cmd | -m mod | file] [--] [arg] ...
If invoked with no options, it executes the file and exits, passing the
remaining arguments to the script, just as if you had specified the same
command with python. You may need to specify `--` before args to be passed
to the script, to prevent IPython from attempting to parse them. If you
specify the option `-i` before the filename, it will enter an interactive
IPython session after running the script, rather than exiting. Files ending
in .py will be treated as normal Python, but files ending in .ipy can
contain special IPython syntax (magic commands, shell expansions, etc.).
Almost all configuration in IPython is available via the command-line. Do
`ipython --help-all` to see all available options. For persistent
configuration, look into your `ipython_config.py` configuration file for
details.
This file is typically installed in the `IPYTHONDIR` directory, and there
is a separate configuration directory for each profile. The default profile
directory will be located in $IPYTHONDIR/profile_default. IPYTHONDIR
defaults to to `$HOME/.ipython`. For Windows users, $HOME resolves to
C:\Users\YourUserName in most instances.
To initialize a profile with the default configuration file, do::
$> ipython profile create
and start editing `IPYTHONDIR/profile_default/ipython_config.py`
In IPython's documentation, we will refer to this directory as
`IPYTHONDIR`, you can change its default location by creating an
environment variable with this name and setting it to the desired path.
For more information, see the manual available in HTML and PDF in your
installation, or online at http://ipython.org/documentation.html.
Subcommands
-----------
Subcommands are launched as `ipython cmd [args]`. For information on using
subcommand 'cmd', do: `ipython cmd -h`.
profile
Create and manage IPython profiles.
kernel
Start a kernel without an attached frontend.
locate
print the path to the IPython dir
history
Manage the IPython history database.
qtconsole
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Launch the Jupyter Qt Console.
notebook
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Launch the Jupyter HTML Notebook Server.
console
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Launch the Jupyter terminal-based Console.
nbconvert
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Convert notebooks to/from other formats.
trust
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Sign notebooks to trust their potentially unsafe contents at load.
kernelspec
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Manage Jupyter kernel specifications.
install-nbextension
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Install Jupyter notebook extension files
Options
-------
Arguments that take values are actually convenience aliases to full
Configurables, whose aliases are listed on the help line. For more information
on full configurables, see '--help-all'.
--debug
set log level to logging.DEBUG (maximize logging output)
--quiet
set log level to logging.CRITICAL (minimize logging output)
--init
Initialize profile with default config files. This is equivalent
to running `ipython profile create <profile>` prior to startup.
--autoindent
Turn on autoindenting.
--no-autoindent
Turn off autoindenting.
--automagic
Turn on the auto calling of magic commands. Type %%magic at the
IPython prompt for more information.
--no-automagic
Turn off the auto calling of magic commands.
--pdb
Enable auto calling the pdb debugger after every exception.
--no-pdb
Disable auto calling the pdb debugger after every exception.
--pprint
Enable auto pretty printing of results.
--no-pprint
Disable auto pretty printing of results.
--color-info
IPython can display information about objects via a set of functions,
and optionally can use colors for this, syntax highlighting
source code and various other elements. This is on by default, but can cause
problems with some pagers. If you see such problems, you can disable the
colours.
--no-color-info
Disable using colors for info related things.
--nosep
Eliminate all spacing between prompts.
--pylab
Pre-load matplotlib and numpy for interactive use with
the default matplotlib backend.
--matplotlib
Configure matplotlib for interactive use with
the default matplotlib backend.
--autoedit-syntax
Turn on auto editing of files with syntax errors.
--no-autoedit-syntax
Turn off auto editing of files with syntax errors.
--simple-prompt
Force simple minimal prompt using `raw_input`
--no-simple-prompt
Use a rich interactive prompt with prompt_toolkit
--banner
Display a banner upon starting IPython.
--no-banner
Don't display a banner upon starting IPython.
--confirm-exit
Set to confirm when you try to exit IPython with an EOF (Control-D
in Unix, Control-Z/Enter in Windows). By typing 'exit' or 'quit',
you can force a direct exit without any confirmation.
--no-confirm-exit
Don't prompt the user when exiting.
--term-title
Enable auto setting the terminal title.
--no-term-title
Disable auto setting the terminal title.
--classic
Gives IPython a similar feel to the classic Python prompt.
--quick
Enable quick startup with no config files.
-i
If running code from the command line, become interactive afterwards.
It is often useful to follow this with `--` to treat remaining flags as
script arguments.
--profile-dir=<Unicode> (ProfileDir.location)
Default: ''
Set the profile location directly. This overrides the logic used by the
`profile` option.
--profile=<Unicode> (BaseIPythonApplication.profile)
Default: 'default'
The IPython profile to use.
--ipython-dir=<Unicode> (BaseIPythonApplication.ipython_dir)
Default: ''
The name of the IPython directory. This directory is used for logging
configuration (through profiles), history storage, etc. The default is
usually $HOME/.ipython. This option can also be specified through the
environment variable IPYTHONDIR.
--log-level=<Enum> (Application.log_level)
Default: 30
Choices: (0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 'DEBUG', 'INFO', 'WARN', 'ERROR', 'CRITICAL')
Set the log level by value or name.
--config=<Unicode> (BaseIPythonApplication.extra_config_file)
Default: ''
Path to an extra config file to load.
If specified, load this config file in addition to any other IPython config.
--autocall=<Enum> (InteractiveShell.autocall)
Default: 0
Choices: (0, 1, 2)
Make IPython automatically call any callable object even if you didn't type
explicit parentheses. For example, 'str 43' becomes 'str(43)' automatically.
The value can be '0' to disable the feature, '1' for 'smart' autocall, where
it is not applied if there are no more arguments on the line, and '2' for
'full' autocall, where all callable objects are automatically called (even
if no arguments are present).
--colors=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShell.colors)
Default: 'Neutral'
Choices: ['Neutral', 'NoColor', 'LightBG', 'Linux']
Set the color scheme (NoColor, Neutral, Linux, or LightBG).
--logfile=<Unicode> (InteractiveShell.logfile)
Default: ''
The name of the logfile to use.
--logappend=<Unicode> (InteractiveShell.logappend)
Default: ''
Start logging to the given file in append mode. Use `logfile` to specify a
log file to **overwrite** logs to.
-c <Unicode> (InteractiveShellApp.code_to_run)
Default: ''
Execute the given command string.
-m <Unicode> (InteractiveShellApp.module_to_run)
Default: ''
Run the module as a script.
--ext=<Unicode> (InteractiveShellApp.extra_extension)
Default: ''
dotted module name of an IPython extension to load.
--gui=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShellApp.gui)
Default: None
Choices: ['glut', 'gtk', 'gtk2', 'gtk3', 'osx', 'pyglet', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'wx', 'gtk2', 'qt4']
Enable GUI event loop integration with any of ('glut', 'gtk', 'gtk2',
'gtk3', 'osx', 'pyglet', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'wx', 'gtk2', 'qt4').
--pylab=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShellApp.pylab)
Default: None
Choices: ['auto', 'agg', 'gtk', 'gtk3', 'inline', 'ipympl', 'nbagg', 'notebook', 'osx', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'widget', 'wx']
Pre-load matplotlib and numpy for interactive use, selecting a particular
matplotlib backend and loop integration.
--matplotlib=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShellApp.matplotlib)
Default: None
Choices: ['auto', 'agg', 'gtk', 'gtk3', 'inline', 'ipympl', 'nbagg', 'notebook', 'osx', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'widget', 'wx']
Configure matplotlib for interactive use with the default matplotlib
backend.
--cache-size=<Int> (InteractiveShell.cache_size)
Default: 1000
Set the size of the output cache. The default is 1000, you can change it
permanently in your config file. Setting it to 0 completely disables the
caching system, and the minimum value accepted is 3 (if you provide a value
less than 3, it is reset to 0 and a warning is issued). This limit is
defined because otherwise you'll spend more time re-flushing a too small
cache than working
To see all available configurables, use `--help-all`
Examples
--------
ipython --matplotlib # enable matplotlib integration
ipython --matplotlib=qt # enable matplotlib integration with qt4 backend
ipython --log-level=DEBUG # set logging to DEBUG
ipython --profile=foo # start with profile foo
ipython profile create foo # create profile foo w/ default config files
ipython help profile # show the help for the profile subcmd
ipython locate # print the path to the IPython directory
ipython locate profile foo # print the path to the directory for profile `foo`
- Some error happened while getting info on the interpreter:
java.lang.RuntimeException: Unable to recreate the Interpreter info (Its format changed. Please, re-create your Interpreter information).Contents found:=========
IPython
=========
Tools for Interactive Computing in Python
=========================================
A Python shell with automatic history (input and output), dynamic object
introspection, easier configuration, command completion, access to the
system shell and more. IPython can also be embedded in running programs.
Usage
ipython [subcommand] [options] [-c cmd | -m mod | file] [--] [arg] ...
If invoked with no options, it executes the file and exits, passing the
remaining arguments to the script, just as if you had specified the same
command with python. You may need to specify `--` before args to be passed
to the script, to prevent IPython from attempting to parse them. If you
specify the option `-i` before the filename, it will enter an interactive
IPython session after running the script, rather than exiting. Files ending
in .py will be treated as normal Python, but files ending in .ipy can
contain special IPython syntax (magic commands, shell expansions, etc.).
Almost all configuration in IPython is available via the command-line. Do
`ipython --help-all` to see all available options. For persistent
configuration, look into your `ipython_config.py` configuration file for
details.
This file is typically installed in the `IPYTHONDIR` directory, and there
is a separate configuration directory for each profile. The default profile
directory will be located in $IPYTHONDIR/profile_default. IPYTHONDIR
defaults to to `$HOME/.ipython`. For Windows users, $HOME resolves to
C:\Users\YourUserName in most instances.
To initialize a profile with the default configuration file, do::
$> ipython profile create
and start editing `IPYTHONDIR/profile_default/ipython_config.py`
In IPython's documentation, we will refer to this directory as
`IPYTHONDIR`, you can change its default location by creating an
environment variable with this name and setting it to the desired path.
For more information, see the manual available in HTML and PDF in your
installation, or online at http://ipython.org/documentation.html.
Subcommands
-----------
Subcommands are launched as `ipython cmd [args]`. For information on using
subcommand 'cmd', do: `ipython cmd -h`.
profile
Create and manage IPython profiles.
kernel
Start a kernel without an attached frontend.
locate
print the path to the IPython dir
history
Manage the IPython history database.
qtconsole
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Launch the Jupyter Qt Console.
notebook
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Launch the Jupyter HTML Notebook Server.
console
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Launch the Jupyter terminal-based Console.
nbconvert
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Convert notebooks to/from other formats.
trust
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Sign notebooks to trust their potentially unsafe contents at load.
kernelspec
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Manage Jupyter kernel specifications.
install-nbextension
DEPRECATED, Will be removed in IPython 6.0 : Install Jupyter notebook extension files
Options
-------
Arguments that take values are actually convenience aliases to full
Configurables, whose aliases are listed on the help line. For more information
on full configurables, see '--help-all'.
--debug
set log level to logging.DEBUG (maximize logging output)
--quiet
set log level to logging.CRITICAL (minimize logging output)
--init
Initialize profile with default config files. This is equivalent
to running `ipython profile create <profile>` prior to startup.
--autoindent
Turn on autoindenting.
--no-autoindent
Turn off autoindenting.
--automagic
Turn on the auto calling of magic commands. Type %%magic at the
IPython prompt for more information.
--no-automagic
Turn off the auto calling of magic commands.
--pdb
Enable auto calling the pdb debugger after every exception.
--no-pdb
Disable auto calling the pdb debugger after every exception.
--pprint
Enable auto pretty printing of results.
--no-pprint
Disable auto pretty printing of results.
--color-info
IPython can display information about objects via a set of functions,
and optionally can use colors for this, syntax highlighting
source code and various other elements. This is on by default, but can cause
problems with some pagers. If you see such problems, you can disable the
colours.
--no-color-info
Disable using colors for info related things.
--nosep
Eliminate all spacing between prompts.
--pylab
Pre-load matplotlib and numpy for interactive use with
the default matplotlib backend.
--matplotlib
Configure matplotlib for interactive use with
the default matplotlib backend.
--autoedit-syntax
Turn on auto editing of files with syntax errors.
--no-autoedit-syntax
Turn off auto editing of files with syntax errors.
--simple-prompt
Force simple minimal prompt using `raw_input`
--no-simple-prompt
Use a rich interactive prompt with prompt_toolkit
--banner
Display a banner upon starting IPython.
--no-banner
Don't display a banner upon starting IPython.
--confirm-exit
Set to confirm when you try to exit IPython with an EOF (Control-D
in Unix, Control-Z/Enter in Windows). By typing 'exit' or 'quit',
you can force a direct exit without any confirmation.
--no-confirm-exit
Don't prompt the user when exiting.
--term-title
Enable auto setting the terminal title.
--no-term-title
Disable auto setting the terminal title.
--classic
Gives IPython a similar feel to the classic Python prompt.
--quick
Enable quick startup with no config files.
-i
If running code from the command line, become interactive afterwards.
It is often useful to follow this with `--` to treat remaining flags as
script arguments.
--profile-dir=<Unicode> (ProfileDir.location)
Default: ''
Set the profile location directly. This overrides the logic used by the
`profile` option.
--profile=<Unicode> (BaseIPythonApplication.profile)
Default: 'default'
The IPython profile to use.
--ipython-dir=<Unicode> (BaseIPythonApplication.ipython_dir)
Default: ''
The name of the IPython directory. This directory is used for logging
configuration (through profiles), history storage, etc. The default is
usually $HOME/.ipython. This option can also be specified through the
environment variable IPYTHONDIR.
--log-level=<Enum> (Application.log_level)
Default: 30
Choices: (0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 'DEBUG', 'INFO', 'WARN', 'ERROR', 'CRITICAL')
Set the log level by value or name.
--config=<Unicode> (BaseIPythonApplication.extra_config_file)
Default: ''
Path to an extra config file to load.
If specified, load this config file in addition to any other IPython config.
--autocall=<Enum> (InteractiveShell.autocall)
Default: 0
Choices: (0, 1, 2)
Make IPython automatically call any callable object even if you didn't type
explicit parentheses. For example, 'str 43' becomes 'str(43)' automatically.
The value can be '0' to disable the feature, '1' for 'smart' autocall, where
it is not applied if there are no more arguments on the line, and '2' for
'full' autocall, where all callable objects are automatically called (even
if no arguments are present).
--colors=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShell.colors)
Default: 'Neutral'
Choices: ['Neutral', 'NoColor', 'LightBG', 'Linux']
Set the color scheme (NoColor, Neutral, Linux, or LightBG).
--logfile=<Unicode> (InteractiveShell.logfile)
Default: ''
The name of the logfile to use.
--logappend=<Unicode> (InteractiveShell.logappend)
Default: ''
Start logging to the given file in append mode. Use `logfile` to specify a
log file to **overwrite** logs to.
-c <Unicode> (InteractiveShellApp.code_to_run)
Default: ''
Execute the given command string.
-m <Unicode> (InteractiveShellApp.module_to_run)
Default: ''
Run the module as a script.
--ext=<Unicode> (InteractiveShellApp.extra_extension)
Default: ''
dotted module name of an IPython extension to load.
--gui=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShellApp.gui)
Default: None
Choices: ['glut', 'gtk', 'gtk2', 'gtk3', 'osx', 'pyglet', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'wx', 'gtk2', 'qt4']
Enable GUI event loop integration with any of ('glut', 'gtk', 'gtk2',
'gtk3', 'osx', 'pyglet', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'wx', 'gtk2', 'qt4').
--pylab=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShellApp.pylab)
Default: None
Choices: ['auto', 'agg', 'gtk', 'gtk3', 'inline', 'ipympl', 'nbagg', 'notebook', 'osx', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'widget', 'wx']
Pre-load matplotlib and numpy for interactive use, selecting a particular
matplotlib backend and loop integration.
--matplotlib=<CaselessStrEnum> (InteractiveShellApp.matplotlib)
Default: None
Choices: ['auto', 'agg', 'gtk', 'gtk3', 'inline', 'ipympl', 'nbagg', 'notebook', 'osx', 'qt', 'qt4', 'qt5', 'tk', 'widget', 'wx']
Configure matplotlib for interactive use with the default matplotlib
backend.
--cache-size=<Int> (InteractiveShell.cache_size)
Default: 1000
Set the size of the output cache. The default is 1000, you can change it
permanently in your config file. Setting it to 0 completely disables the
caching system, and the minimum value accepted is 3 (if you provide a value
less than 3, it is reset to 0 and a warning is issued). This limit is
defined because otherwise you'll spend more time re-flushing a too small
cache than working
To see all available configurables, use `--help-all`
Examples
--------
ipython --matplotlib # enable matplotlib integration
ipython --matplotlib=qt # enable matplotlib integration with qt4 backend
ipython --log-level=DEBUG # set logging to DEBUG
ipython --profile=foo # start with profile foo
ipython profile create foo # create profile foo w/ default config files
ipython help profile # show the help for the profile subcmd
ipython locate # print the path to the IPython directory
ipython locate profile foo # print the path to the directory for profile `foo`
at org.python.pydev.ui.pythonpathconf.InterpreterInfo.fromString(InterpreterInfo.java:287)
at org.python.pydev.ui.interpreters.AbstractInterpreterManager.createInfoFromOutput(AbstractInterpreterManager.java:422)
at org.python.pydev.ui.interpreters.PythonInterpreterManager.doCreateInterpreterInfo(PythonInterpreterManager.java:72)
at org.python.pydev.ui.interpreters.PythonInterpreterManager.internalCreateInterpreterInfo(PythonInterpreterManager.java:45)
at org.python.pydev.ui.interpreters.AbstractInterpreterManager.createInterpreterInfo(AbstractInterpreterManager.java:369)
at org.python.pydev.ui.pythonpathconf.ObtainInterpreterInfoOperation.run(ObtainInterpreterInfoOperation.java:78)
at org.eclipse.jface.operation.ModalContext$ModalContextThread.run(ModalContext.java:121)
at org.python.pydev.core.log.Log.logInfo(Log.java:62)
at org.python.pydev.ui.pythonpathconf.AbstractInterpreterEditor.getNewInputObject(AbstractInterpreterEditor.java:1074)
at org.python.copiedfromeclipsesrc.PythonListEditor.addPressed(PythonListEditor.java:135)
at org.python.copiedfromeclipsesrc.PythonListEditor$1.widgetSelected(PythonListEditor.java:225)
at org.eclipse.swt.widgets.TypedListener.handleEvent(TypedListener.java:240)
at org.eclipse.swt.widgets.EventTable.sendEvent(EventTable.java:84)
at org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Widget.sendEvent(Widget.java:1053)
at org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display.runDeferredEvents(Display.java:4165)
at org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display.readAndDispatch(Display.java:3754)
at org.eclipse.jface.window.Window.runEventLoop(Window.java:825)
at org.eclipse.jface.window.Window.open(Window.java:801)
at org.eclipse.ui.internal.dialogs.WorkbenchPreferenceDialog.open(WorkbenchPreferenceDialog.java:215)
at org.eclipse.ui.internal.handlers.ShowPreferencePageHandler.execute(ShowPreferencePageHandler.java:54)
at org.eclipse.ui.internal.handlers.HandlerProxy.execute(HandlerProxy.java:293)
at org.eclipse.core.commands.Command.executeWithChecks(Command.java:476)
at org.eclipse.core.commands.ParameterizedCommand.executeWithChecks(ParameterizedCommand.java:508)
at org.eclipse.ui.internal.handlers.HandlerService.executeCommand(HandlerService.java:169)
at org.eclipse.ui.internal.handlers.SlaveHandlerService.executeCommand(SlaveHandlerService.java:241)
at org.eclipse.ui.internal.actions.CommandAction.runWithEvent(CommandAction.java:157)
at org.eclipse.jface.action.ActionContributionItem.handleWidgetSelection(ActionContributionItem.java:584)
at org.eclipse.jface.action.ActionContributionItem.access$2(ActionContributionItem.java:501)
at org.eclipse.jface.action.ActionContributionItem$5.handleEvent(ActionContributionItem.java:411)
at org.eclipse.swt.widgets.EventTable.sendEvent(EventTable.java:84)
at org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Widget.sendEvent(Widget.java:1053)
at org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display.runDeferredEvents(Display.java:4165)
at org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display.readAndDispatch(Display.java:3754)
at org.eclipse.ui.internal.Workbench.runEventLoop(Workbench.java:2701)
at org.eclipse.ui.internal.Workbench.runUI(Workbench.java:2665)
at org.eclipse.ui.internal.Workbench.access$4(Workbench.java:2499)
at org.eclipse.ui.internal.Workbench$7.run(Workbench.java:679)
at org.eclipse.core.databinding.observable.Realm.runWithDefault(Realm.java:332)
at org.eclipse.ui.internal.Workbench.createAndRunWorkbench(Workbench.java:668)
at org.eclipse.ui.PlatformUI.createAndRunWorkbench(PlatformUI.java:149)
at com.aptana.rcp.IDEApplication.start(IDEApplication.java:125)
at org.eclipse.equinox.internal.app.EclipseAppHandle.run(EclipseAppHandle.java:196)
at org.eclipse.core.runtime.internal.adaptor.EclipseAppLauncher.runApplication(EclipseAppLauncher.java:110)
at org.eclipse.core.runtime.internal.adaptor.EclipseAppLauncher.start(EclipseAppLauncher.java:79)
at org.eclipse.core.runtime.adaptor.EclipseStarter.run(EclipseStarter.java:344)
at org.eclipse.core.runtime.adaptor.EclipseStarter.run(EclipseStarter.java:179)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(Unknown Source)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(Unknown Source)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Unknown Source)
at org.eclipse.equinox.launcher.Main.invokeFramework(Main.java:622)
at org.eclipse.equinox.launcher.Main.basicRun(Main.java:577)
at org.eclipse.equinox.launcher.Main.run(Main.java:1410)
Отредактировано @cckyi_boxxx (Дек. 22, 2018 11:58:22)
Офлайн
#6 Дек. 22, 2018 13:22:32
- PEHDOM
-

-

- Зарегистрирован: 2016-11-28
- Сообщения: 2196
- Репутация:
 294
294 
- Профиль Отправить e-mail
Pydev + IPython
ну вобщем шоб сказать чтото определенное так нет, но ИМХО это изза того что у вас два пайтона, и гдето используеться пайтон одной версии а либы и/или инфо из другой.
вобщем выдкржка из мануала тоже говорит чтото подобное, нужно разбираться с вашими переменными окружения.
What if it is not correct?
The most common error is having a problem in the environment variables used from the shell that spawned Eclipse, in a way that for some reason when getting the variables of one interpreter, it gathers the info from another interpreter (thus mixing the interpreter and the actual libraries).
Usually running (from the command prompt) the file that gives that info for PyDev can help you discovering the problem in your configuration (interpreterInfo.py):
That file is usually located at: eclipse\plugins\org.python.pydev_$version$\pysrc\interpreterInfo.py, but it can be at other location depending on how you installed it )
In Python: python.exe interpreterInfo.py
In Jython: java.exe -cp c:\path\to\jython.jar org.python.util.jython interpreterInfo.py
In IronPython: ipy.exe interpreterInfo.py
If you're unable to find out what's going on, please open an issue in the tracker (https://www.brainwy.com/tracker/PyDev (giving the output obtained from executing interpreterInfo.py in your machine).
==============================
Помещайте код в теги:
[code python][/code]
Офлайн
#7 Дек. 22, 2018 13:49:37
- @cckyi_boxxx
-

-
- От:
- Зарегистрирован: 2012-01-13
- Сообщения: 181
- Репутация:
 14
14 
- Профиль Отправить e-mail
Pydev + IPython
ставил и по 3 интерпретатора, все работало
попробовал тут руками запустить проблемный скрипт на ipython и на чистом питоне ,
C:\Users\devlapt>ipython "C:\Users\devlapt\AppData\Local\Aptana Studio 3\plugins\org.python.pydev_2.7.0.2013032300\pysrc\interpreterInfo.py"
<xml>
<version>3.6</version>
<executable>c:\program files\python36\python.exe</executable>
<lib path="out">C:\Users\devlapt\AppData\Local\Aptana Studio 3\plugins\org.python.pydev_2.7.0.2013032300\pysrc</lib>
<lib path="out">.</lib>
<lib path="out">C:\Program Files\Python36\Scripts\ipython.exe</lib>
<lib path="ins">c:\program files\python36\python36.zip</lib>
<lib path="ins">c:\program files\python36\DLLs</lib>
<lib path="ins">c:\program files\python36\lib</lib>
<lib path="ins">c:\program files\python36</lib>
<lib path="ins">c:\program files\python36\lib\site-packages</lib>
<lib path="ins">c:\program files\python36\lib\site-packages\win32</lib>
<lib path="ins">c:\program files\python36\lib\site-packages\win32\lib</lib>
<lib path="ins">c:\program files\python36\lib\site-packages\Pythonwin</lib>
<lib path="ins">c:\program files\python36\lib\site-packages\IPython\extensions</lib>
<lib path="out">C:\Users\devlapt\.ipython</lib>
<forced_lib>_ast</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_bisect</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_blake2</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_codecs</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_codecs_cn</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_codecs_hk</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_codecs_iso2022</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_codecs_jp</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_codecs_kr</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_codecs_tw</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_collections</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_csv</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_datetime</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_findvs</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_functools</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_heapq</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_imp</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_io</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_json</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_locale</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_lsprof</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_md5</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_multibytecodec</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_opcode</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_operator</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_pickle</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_random</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_sha1</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_sha256</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_sha3</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_sha512</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_signal</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_sre</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_stat</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_string</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_struct</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_symtable</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_thread</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_tracemalloc</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_warnings</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_weakref</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>_winapi</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>array</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>atexit</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>audioop</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>binascii</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>builtins</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>cmath</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>errno</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>faulthandler</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>gc</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>itertools</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>marshal</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>math</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>mmap</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>msvcrt</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>nt</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>parser</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>sys</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>time</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>winreg</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>xxsubtype</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>zipimport</forced_lib>
<forced_lib>zlib</forced_lib>
</xml>---------------------------------------------------------------------------
RuntimeError Traceback (most recent call last)
~\AppData\Local\Aptana Studio 3\plugins\org.python.pydev_2.7.0.2013032300\pysrc\interpreterInfo.py in <module>()
197 pass
198
--> 199 raise RuntimeError('Ok, this is so that it shows the output (ugly hack for some platforms, so that it releases the output).')
RuntimeError: Ok, this is so that it shows the output (ugly hack for some platforms, so that it releases the output).
C:\Users\devlapt>
вот код этого скрипта
''' This module was created to get information available in the interpreter, such as libraries, paths, etc. what is what: sys.builtin_module_names: contains the builtin modules embeeded in python (rigth now, we specify all manually). sys.prefix: A string giving the site-specific directory prefix where the platform independent Python files are installed format is something as EXECUTABLE:python.exe|libs@compiled_dlls$builtin_mods all internal are separated by | ''' import sys try: import os.path def fullyNormalizePath(path): '''fixes the path so that the format of the path really reflects the directories in the system ''' return os.path.normpath(path) join = os.path.join except: #ImportError or AttributeError. #See: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/10254353/error-while-installing-jython-for-pydev def fullyNormalizePath(path): '''fixes the path so that the format of the path really reflects the directories in the system ''' return path def join(a, b): if a.endswith('/') or a.endswith('\\'): return a + b return a + '/' + b IS_PYTHON_3K = 0 try: if sys.version_info[0] == 3: IS_PYTHON_3K = 1 except: #That's OK, not all versions of python have sys.version_info pass try: #Just check if False and True are defined (depends on version, not whether it's jython/python) False True except: exec ('True, False = 1,0') #An exec is used so that python 3k does not give a syntax error import time if sys.platform == "cygwin": try: import ctypes #use from the system if available except ImportError: sys.path.append(join(sys.path[0], 'third_party/wrapped_for_pydev')) import ctypes def nativePath(path): MAX_PATH = 512 # On cygwin NT, its 260 lately, but just need BIG ENOUGH buffer '''Get the native form of the path, like c:\\Foo for /cygdrive/c/Foo''' retval = ctypes.create_string_buffer(MAX_PATH) path = fullyNormalizePath(path) ctypes.cdll.cygwin1.cygwin_conv_to_win32_path(path, retval) #@UndefinedVariable return retval.value else: def nativePath(path): return fullyNormalizePath(path) def getfilesystemencoding(): try: ret = sys.getfilesystemencoding() if not ret: raise RuntimeError('Unable to get encoding.') return ret except: #Only available from 2.3 onwards. if sys.platform == 'win32': return 'mbcs' return 'utf-8' file_system_encoding = getfilesystemencoding() def tounicode(s): if hasattr(s, 'decode'): #Depending on the platform variant we may have decode on string or not. return s.decode(file_system_encoding) return s def toutf8(s): if hasattr(s, 'encode'): return s.encode('utf-8') return s if __name__ == '__main__': try: #just give some time to get the reading threads attached (just in case) time.sleep(0.1) except: pass try: executable = nativePath(sys.executable) except: executable = sys.executable if sys.platform == "cygwin" and not executable.endswith('.exe'): executable += '.exe' try: major = str(sys.version_info[0]) minor = str(sys.version_info[1]) except AttributeError: #older versions of python don't have version_info import string s = string.split(sys.version, ' ')[0] s = string.split(s, '.') major = s[0] minor = s[1] s = tounicode('%s.%s') % (tounicode(major), tounicode(minor)) contents = [tounicode('<xml>')] contents.append(tounicode('<version>%s</version>') % (tounicode(s),)) contents.append(tounicode('<executable>%s</executable>') % tounicode(executable)) #this is the new implementation to get the system folders #(still need to check if it works in linux) #(previously, we were getting the executable dir, but that is not always correct...) prefix = tounicode(nativePath(sys.prefix)) #print_ 'prefix is', prefix result = [] path_used = sys.path try: path_used = path_used[:] #Use a copy. except: pass #just ignore it... for p in path_used: p = tounicode(nativePath(p)) try: import string #to be compatible with older versions if string.find(p, prefix) == 0: #was startswith result.append((p, True)) else: result.append((p, False)) except (ImportError, AttributeError): #python 3k also does not have it #jython may not have it (depending on how are things configured) if p.startswith(prefix): #was startswith result.append((p, True)) else: result.append((p, False)) for p, b in result: if b: contents.append(tounicode('<lib path="ins">%s</lib>') % (p,)) else: contents.append(tounicode('<lib path="out">%s</lib>') % (p,)) #no compiled libs #nor forced libs for builtinMod in sys.builtin_module_names: contents.append(tounicode('<forced_lib>%s</forced_lib>') % tounicode(builtinMod)) contents.append(tounicode('</xml>')) unic = tounicode('\n').join(contents) inutf8 = toutf8(unic) if IS_PYTHON_3K: #This is the 'official' way of writing binary output in Py3K (see: http://bugs.python.org/issue4571) sys.stdout.buffer.write(inutf8) else: sys.stdout.write(inutf8) try: sys.stdout.flush() sys.stderr.flush() #and give some time to let it read things (just in case) time.sleep(0.1) except: pass raise RuntimeError('Ok, this is so that it shows the output (ugly hack for some platforms, so that it releases the output).')
а вот переменные среды, вроде все правильно
'''
Microsoft Windows [Version 6.1.7601]
(c) Корпорация Майкрософт (Microsoft Corp.), 2014. Все права защищены.
C:\Users\devlapt>set
ALLUSERSPROFILE=C:\ProgramData
APPDATA=C:\Users\devlapt\AppData\Roaming
CommonProgramFiles=C:\Program Files\Common Files
CommonProgramFiles(x86)=C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files
CommonProgramW6432=C:\Program Files\Common Files
COMPUTERNAME=DEVLAPT-PC
ComSpec=C:\Windows\system32\cmd.exe
FP_NO_HOST_CHECK=NO
HOMEDRIVE=C:
HOMEPATH=\Users\devlapt
LOCALAPPDATA=C:\Users\devlapt\AppData\Local
LOGONSERVER=\\DEVLAPT-PC
NUMBER_OF_PROCESSORS=4
OS=Windows_NT
Path=C:\Program Files\Python36\Scripts\;C:\Program Files\Python36\;C:\Program Files (x86)\NVIDIA Corporation\PhysX\Common;C:\Windows\system32;C:\Windows;C:\Windows\System32\Wbem;C:
\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\;C:\Program Files\Intel\WiFi\bin\;C:\Program Files\Common Files\Intel\WirelessCommon\;C:\Program Files\MATLAB\MATLAB Production Server\R201
5a\runtime\win64;C:\Program Files\MATLAB\MATLAB Production Server\R2015a\bin;C:\Program Files\MATLAB\MATLAB Production Server\R2015a\polyspace\bin;C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Ki
ts\8.1\Windows Performance Toolkit\;;C:\Program Files\Microsoft VS Code\bin
PATHEXT=.COM;.EXE;.BAT;.CMD;.VBS;.VBE;.JS;.JSE;.WSF;.WSH;.MSC;.PY;.PYW
PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE=AMD64
PROCESSOR_IDENTIFIER=Intel64 Family 6 Model 37 Stepping 5, GenuineIntel
PROCESSOR_LEVEL=6
PROCESSOR_REVISION=2505
ProgramData=C:\ProgramData
ProgramFiles=C:\Program Files
ProgramFiles(x86)=C:\Program Files (x86)
ProgramW6432=C:\Program Files
PROMPT=$P$G
PSModulePath=C:\Windows\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\Modules\
PUBLIC=C:\Users\Public
SESSIONNAME=Console
SystemDrive=C:
SystemRoot=C:\Windows
TEMP=C:\Temp
TMP=C:\Temp
USERDOMAIN=devlapt-PC
USERNAME=devlapt
USERPROFILE=C:\Users\devlapt
VBOX_MSI_INSTALL_PATH=C:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\
VS140COMNTOOLS=C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio 14.0\Common7\Tools\
windir=C:\Windows
windows_tracing_flags=3
windows_tracing_logfile=C:\BVTBin\Tests\installpackage\csilogfile.log
C:\Users\devlapt>
Отредактировано @cckyi_boxxx (Дек. 22, 2018 13:52:28)
Офлайн
#8 Дек. 22, 2018 15:40:47
- PEHDOM
-

-

- Зарегистрирован: 2016-11-28
- Сообщения: 2196
- Репутация:
 294
294 
- Профиль Отправить e-mail
Pydev + IPython
вас не смущает ?
C:\Users\devlapt>ipython "C:\Users\devlapt\AppData\Local\Aptana Studio 3\plugins\org.python.pydev_2.7.0.2013032300\pysrc\interpreterInfo.py"У вас пайтон 3.6 а плагин под 2.7, ХЗ может конечно так и надо, но больше ничего криминального я пока не вижу.
<xml>
<version>3.6</version>
<executable>c:\program files\python36\python.exe</executable>
<lib path=“out”>C:\Users\devlapt\AppData\Local\Aptana Studio 3\plugins\org.python.pydev_2.7.0.2013032300\pysrc</lib>
==============================
Помещайте код в теги:
[code python][/code]
Офлайн
#9 Дек. 22, 2018 16:41:38
- @cckyi_boxxx
-

-
- От:
- Зарегистрирован: 2012-01-13
- Сообщения: 181
- Репутация:
 14
14 
- Профиль Отправить e-mail
Pydev + IPython
Обычную версию питона 3.6 плагин скушал на ура, а вот интерактивную ipython не ест зараза.
Попробую пойти другим путем, поищу возможность добавить в aptana studio на панель кнопку с произвольной командой, и в ней уже буду вызывать консоль венды в которой будет запускаться скрипт через ipython, или вовсе создам пару скриптов на питоне, один для запуска на ipython, второй для дебага на ipdb, это конечно наикривейший костыль но хоть что-то.
Отредактировано @cckyi_boxxx (Дек. 22, 2018 16:42:26)
Офлайн
- Начало
- » Инструментальные средства разработки
-
» Pydev + IPython
![[RSS Feed] [RSS Feed]](/static/djangobb_forum/img/feed-icon-small.png)
